
Beyond the Basics of HTML/CSS
Class 3
Welcome!
Girl Develop It is here to provide affordable and accessible programs to learn software through mentorship and hands-on instruction.
Some "rules"
- We are here for you!
- Every question is important
- Help each other
- Have fun
Microdata
Microdata
Micro-what?
From the W3C spec:
Sometimes, it is desirable to annotate content with specific machine-readable labels...
Microdata allows nested groups of namevalue pairs to be added to documents, in parallel with the existing content.Microdata Overview
Microdata
Sounds BORING
Why should I care?

Microdata
Wouldn't it be great if the search results for your restaurant looked like this?

Microdata
Or if search results for your book looked like this?

Microdata
Or if search results for your recipe looked like this?
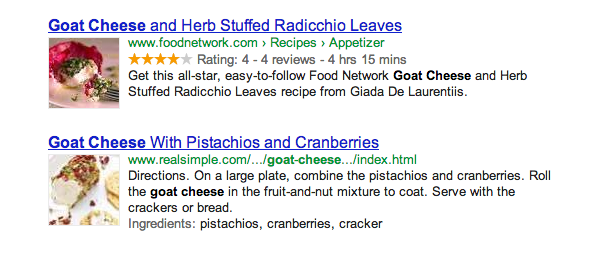
Rich Snippets
The more information a search result snippet can provide, the easier it is for users to decide whether that page is relevant to their search.Rich snippets
Rich Snippets
With rich snippets, webmasters with sites containing structured content...can label their content to make it clear that each labeled piece of text represents a certain type of data: for example, a restaurant name, an address, or a rating.Rich snippets
Microdata Structure
We will add microdata to our favorite pizza restaurant
<div>
L'Amourita Pizza
Located at 123 Main St, Albuquerque, NM.
Phone: 206-555-1234
<a href="http://pizza.com">http://pizza.com</a>
</div>
Microdata Structure
We need to define three things to add microdata to our sites:
- Itemscope attribute
- Itemtype attribute
- Itemprop attribute
Microdata Structure
Itemscope
<div itemscope>
L'Amourita Pizza
Located at 123 Main St, Albuquerque, NM.
Phone: 206-555-1234
<a href="http://pizza.com">http://pizza.com</a>
</div>
Microdata Structure
Item scope
Sets the "scope" of what we are describing with the microdata.
All elements nested inside the div with "itemscope" will adhere to the vocabulary we specify with "itemtype". (i.e. person, place, recipe)
Microdata Structure
Itemtype
<div itemscope itemtype="http://schema.org/Organization">
L'Amourita Pizza
Located at 123 Main St, Albuquerque, NM.
Phone: 206-555-1234
<a href="http://pizza.com">http://pizza.com</a>
</div>
Microdata Structure
Itemtype
Points you to the place where a microdata type is defined
Since we're defining a business, we want to point to the definition of an Organization
http://schema.org defines several type including Organization
Microdata Structure
Itemprop
<div itemscope itemtype ="http://schema.org/Organization">
<span itemprop ="name">L'Amourita Pizza</span>
Located at 123 Main St, Albuquerque, NM.
Phone: <span itemprop ="tel">206-555-1234</span>
<a href="http://pizza.com" itemprop ="url">http://pizza.com</a>
</div>
Microdata Structure
Itemprop
Itemprop is a property of your Item's type. The available properties are listed on the relevant page at http://schema.org/docs/schemas
For our Organization example, the available include are: name, url, address, telephone, and location. For the full list: http://schema.org/Organization
Microdata Structure
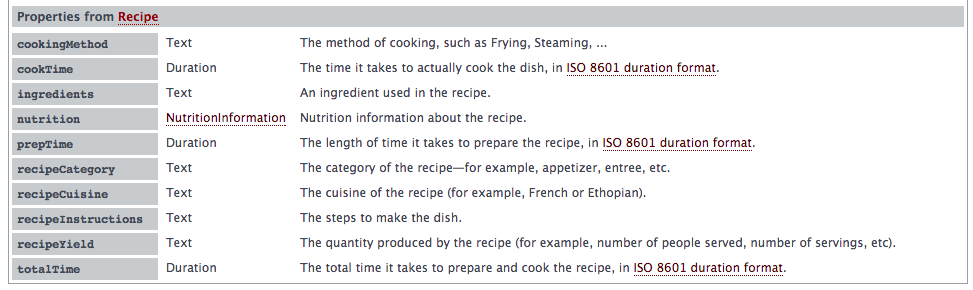
Itemprop
Itemprop is a property of your Item's type. The available properties are listed on the relevant page at http://schema.org/docs/schemas
Here are properties of a Recipe
Nested Microdata
We have specified ALMOST everything for our Organization, but we still don't have entries for the address
<div itemscope itemtype ="http://schema.org/Organization">
<span itemprop ="name">L'Amourita Pizza</span>
Located at 123 Main St, Albuquerque, NM.
Phone: <span itemprop ="tel">206-555-1234</span>
<a href="http://pizza.com" itemprop ="url">http://pizza.com</a>
</div>
Addresses are their own unique itemtype. So we need to nest the address information inside a new element with the itemtype set to Address
Nested Microdata
<div itemscope itemtype ="http://schema.org/Organization">
<span itemprop ="name">L'Amourita Pizza</span>
Located at
<span itemprop ="address" itemscope itemtype ="http://schema.org/PostalAddress">
<span itemprop ="streetAddress">123 Main St</span>,
<span itemprop ="addressLocality">Albuquerque</span>,
<span itemprop ="addressRegion">NM</span>.
</span>
Phone: <span itemprop ="tel">206-555-1234</span>
<a href="http://pizza.com" itemprop ="url">http://pizza.com</a>
</div>
Microdata Resources
- To make sure google sees your page the way you expect (in terms of the microdata), use this tool: http://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/richsnippets
- Getting started guide: http://schema.org/docs/gs.html>
- Tutorial on microdata from Mark Pilgrim: http://diveintohtml5.info/extensibility.html
- Google overview of using Microdata for an Organization: http://www.google.com/support/webmasters/bin/answer.py?answer=146861
Let's Develop It
Enhance our Women in Computing web site to use HTML5 & CSS3
Use the Person schema to describe the women in tech. Feel free to add more info than we have to use more itemprops!
 Multimedia
Multimedia
Audio and video are first class citizens in HTML5
 Multimedia
Multimedia
Useful as a replacement for flash on mobile devices
Flash makes mobile devices sad :(
 Video
Video
The Dream
The video element was created to make it unnecessary to use plugins to display video content on your pages.
The idea is to simplify and streamline video content delivery.
<video src="demo.mp4" type="video/mp4">
Your browser does not support the video element.
</video>
 Video
Video
The Reality
If you want to support ALL browsers and ALL video encodings, you will still need a plugin as a last-resort fall back plan.
This is because not all browsers read video the same way, and older browsers (like IE<9) don't support the video element at all.
 Video
Video
The Reality
<video id="movie" width="320" height="240" preload controls>
<source src="pr6.webm" type='video/webm; codecs="vp8, vorbis"' />
<source src="pr6.ogv" type='video/ogg; codecs="theora, vorbis"' />
<source src="pr6.mp4" />
<object width="320" height="240" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" data="flowplayer-3.2.1.swf">
<param name="movie" value="flowplayer-3.2.1.swf" />
<param name="allowfullscreen" value="true" />
<param name="flashvars" value='config={"clip": {"url": "http://wearehugh.com/dih5/pr6.mp4", "autoPlay":false, "autoBuffering":true}}' />
<p>Download video as <a href="pr6.mp4">MP4</a>, <a href="pr6.webm">WebM</a>, or <a href="pr6.ogv">Ogg</a>.</p>
</object>
</video>
<script>
var v = document.getElementById("movie");
v.onclick = function() {
if (v.paused) {
v.play();
} else {
v.pause();
}
});
</script>
 Audio
Audio
<audio controls>
<source src="music.mp3" type="audio/mpeg"/>
<source src="music.aac" type="audio/mp4" />
<source src="music.ogg" type="audio/ogg"/>
<!-- now include flash fall back -->
</audio>
 Multimedia
Multimedia
If the dream is still far from reality, what's a dev to do?
The good news is, devs are working on it all the time
 Canvas
Canvas
- Environment for creating dynamic images
- Canvas element + javascript = dynamic content!
 Canvas
Canvas
 Canvas
Canvas
The first step is to add a canvas element to your HTML. Make sure you give it an id:
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="400" height="400">
Your browser doesn’t support Canvas.
</canvas>
Unfortunately, everything else (all the cool stuff) is actually in JavaScript and outside the scope of this class
 Device Access
Device Access
Rich, device-aware features and experiences
 Geolocation
Geolocation
Google Map
Browsers using HTML5 can locate you through IP addresses, WiFi connections, and GPS towers (for mobile phones and tablets)
But all the cool interactive stuff is, once again, done in JavaScript
You didn't expect HTML and CSS to do EVERYTHING, did you?
 Storage
Storage
 Storage
Storage
- You can use HTML5 Web Storage to persist simple data.
-
Two kinds of HTML5 Web Storage:
- SessionStorage for per-window data
- LocalStorage for global, persistent data (stored to hard drive through the browser)
 SessionStorage
SessionStorage
- Ever accidentally bought two of the same kind of ticket, because you were shopping the same site in multiple windows/tabs?
- Session Storage provides a good way to prevent this.
- Session Storage is not saved to the user’s hard drive
- It only lasts for the time that a browser window or tab is open and viewing a specific site.
 LocalStorage
LocalStorage
- With Local Storage, we can save data to the user’s computer, via the browser.
- When a user revisits a site in the same browser they first visited in, any data saved to Local Storage can be retrieved.
- Local Storage is browser-specific: Information you save while browsing with Firefox will NOT be available to Safari.